Cloth Simulation
Implementation of Cloth Simulation Using the Mass-Spring and Verlet Models in UE4

Period: September 1, 2022 → December 6, 2022
Last Edited: February 25, 2025, 3:05 PM
Type: Game, Portfolio
Author: MINHA JEON
Tools & Language: Blender, C++, Unreal
State: Done
Description: Implementation of Cloth Simulation using the Mass-Spring and Verlet models in UE4
Participants: 3
Kyung Hee University 2022–2 Game Contents Capstone Design
1️⃣ Overview
- Goal: Develop a 1 vs. 1 fighting game incorporating a Cloth Simulation based on a Mass-Spring model
- Purpose: Enhance the game’s sense of realism and dynamism by introducing realistic cloth behavior
- Key Points
- Study and develop cloth simulation technology that can be applied to a game
- Implement a 1 vs. 1 fighting game with ranged and melee attacks, environment interactions, and distinct animations triggered by different hit locations
- Tools: Visual Studio 2017, UE4 (4.26)
- Role: Implement and optimize the Cloth Simulation, integrate it into the game, troubleshoot issues, and suggest directions for improvement
2️⃣ Survey & Development Process
> Technology
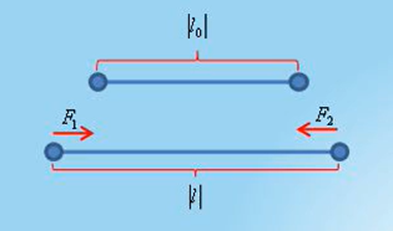
- Cloth Simulation
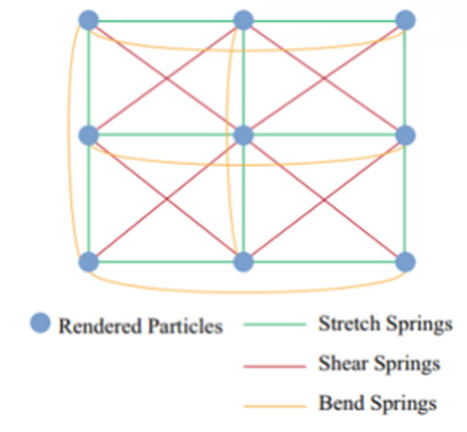
- Mass-Spring Model
- Each vertex of the cloth is treated as a mass (particle), and springs form the connections (edges) between vertices.
- Edge=spring, Vertex=mass
- Use Hook’s law, Newton’s 2nd Law as an equation of motion.
- Particles are connected by several types of spring, which results in a spring force.
- In addition, external force (gravity, wind, collisions with body..) acts to achieve final cloth simulation.
- Basic Cloth Simulation Steps
- Calculating forces (spring, damping, gravity, etc.)
- Integrating positions over time
- Handling collisions and constraints
-
Our Approach
- Used a Mass-Spring model combined with implicit time integration (Backward Euler) for Cloth Simulation
- Created and updated the cloth mesh via procedural mesh in UE4
- Integrated the Eigen library into UE4 to improve computational speed
- Began real-time optimization afterward
-
Issues Encountered
- ⛔ Issue 1: Time Solve & Fix Points
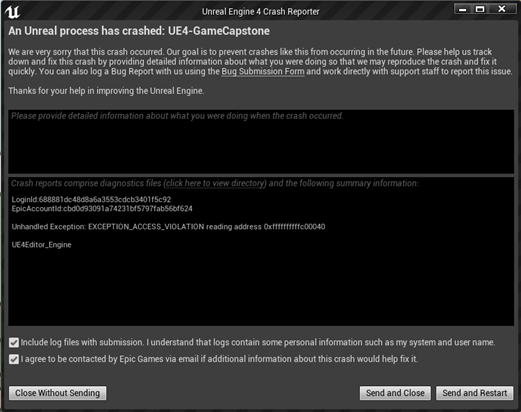
- Encountered errors during the time-solve phase and when fixing anchor points.
- Due to structural differences, null values appeared when using Eigen for computation, preventing proper cloth updates.
- Solved by adjusting the relevant data structures.
- ⛔ Issue 2: Cloth Update
- The cloth converged and did not update correctly at runtime.
- Suspected a mismatch between the Mass-Spring particle indices and the vertex indexing in the procedural mesh.
- Forces were not mapped correctly, causing the cloth to either contract or deform abnormally.
- Time constraints made it difficult to resolve fully, so we decided to pivot to a different integration approach.
- Pivot to PBD & Verlet
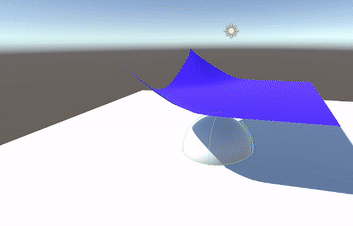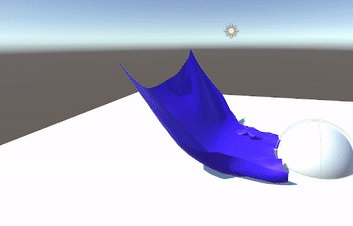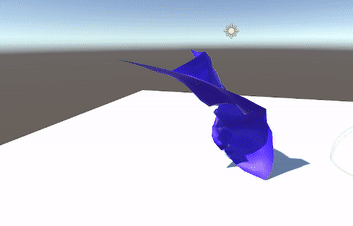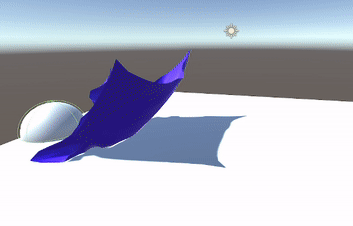
- Position Based Dynamics (PBD)
- Performs physics calculations based on positions rather than velocities, simplifying certain steps.
- Uses a system of constraints directly on particle positions.
- Verlet Integration
- An explicit approach that operates on positions alone.
- No need to store or compute velocity for each particle; updates rely on previous and current positions.
- Constraints are solved by projecting positions directly, rather than by applying forces.
> Game
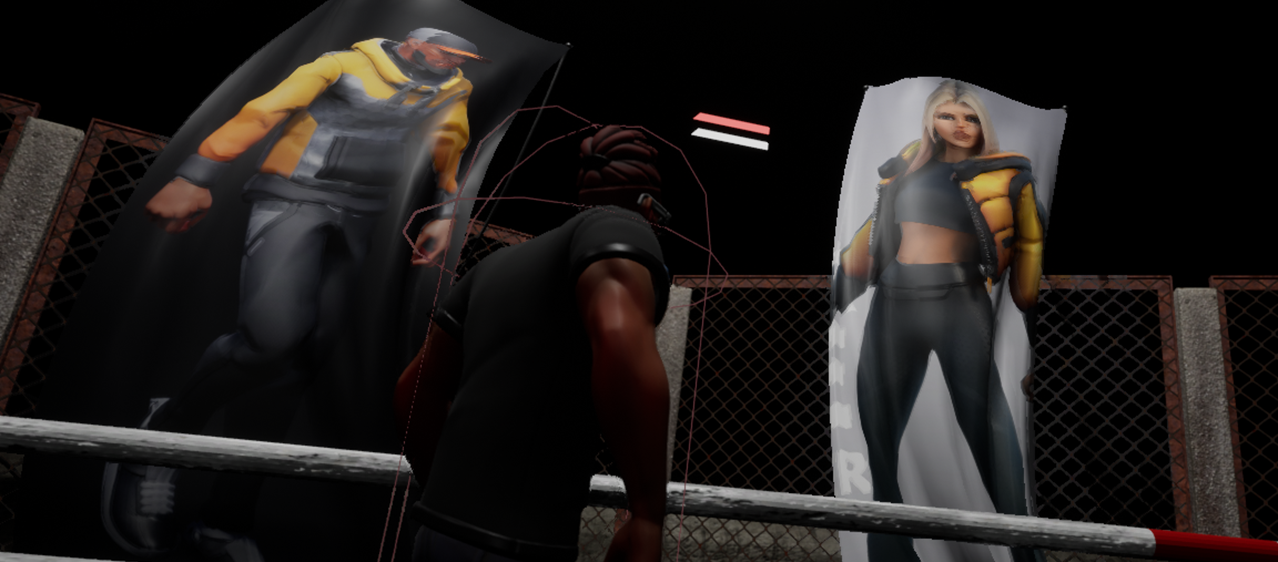
- 1 vs. 1 Fighting Game in an Underground Arena

- Implements an AI opponent that reacts to player actions
- Dodge/Combo system
-
Distinct reactions and hit stops depending on which body part is struck
- Emphasizing Cloth Simulation
- Added banners, flags, and other cloth items to showcase realistic cloth movements
- Cloth items (like towels) scattered around the ring; can be picked up and thrown at the opponent

</div>
</div>
3️⃣ Result
Level of Achievement
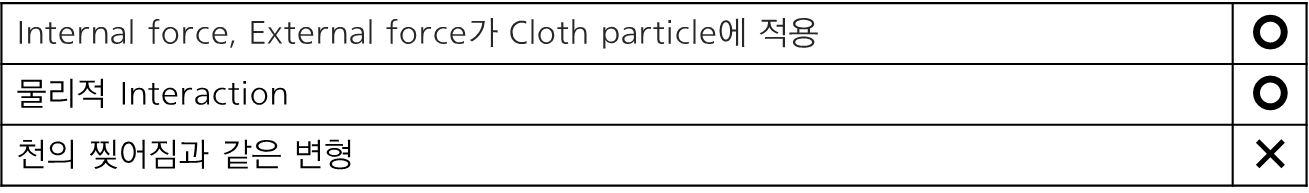

Significance & Limitations
-
Significance
- Cloth Simulation can apply to numerous in-game elements (character clothing, background elements)
- Allows physically driven, more realistic motion compared to purely pre-animated effects
-
Limitations
- Did not implement advanced deformation (e.g., damage or tearing) of cloth during actual combat
- Real-time CPU simulation proved demanding; further performance gains may require GPGPU (GPU-based) solutions
🔗 Related Resources & Links
GitHub
https://github.com/NCTp/GameCapstoneDesignProject
YouTube
[2022-2 GCCD] Team 3 Cloth Simulation
Reference
- Mass-Spring System:
https://github.com/sam007961/FastMassSpring